Due to the capped supply and decentralized build, Bitcoin is scarce and less susceptible to government manipulations and central bank policies that can cause debasement. This makes the cryptocurrency a hedge against inflation and an alternative store of value.
Giants like MicroStrategy and Tesla are now adopting it as an institutional asset. Importantly, Bitcoin historically surged following a positive inflation shock, as experienced with the 2017 and 2025 highs.
However, to make crucial investment decisions, stakeholders still ask:
- Is Bitcoin an inflation hedge?
- How does inflation impact Bitcoin predictions?
- Does the Bitcoin inflation rate matter?
Understanding Inflation: Why It Impacts All Financial Assets
There are three significant types of inflation: core, monetary, and CPI inflation. With core inflation, the rate at which prices are rising, generally excluding prices of volatile commodities like food and energy, is in focus. Monetary inflation basically concerns the sustained increase in money production, creating excess money, while CPI inflation concerns the increase in the average price paid by consumers for food and consumer services.
When money inflation goes high, fiat currencies weaken because their purchasing power decreases. Investors, thereby, pivot to alternative assets like BTC and gold as a store of value and a hedge because they have a limited supply with no central authority and are free from debasement. When investors expect inflation to be high, cash quickly flows from fiat to inflation-resistant assets like Bitcoin and gold, causing price spikes.
Bitcoin’s Inflation Rate Explained — A Predictable, Programmed Monetary Policy
With its supply capped at 21 million and just 3.125 BTC per block as rewards, Bitcoin drives value and asymmetrical investment profits. The number of BTC coins in circulation reduces greatly as the halving cycles keep slashing the amount of BTC by 50% every 4 years. Hence, fiat inflation is unpredictable and policy-driven as the government can print infinite amounts of cash, while Bitcoin inflation is algorithmic and decreases every 4 years.
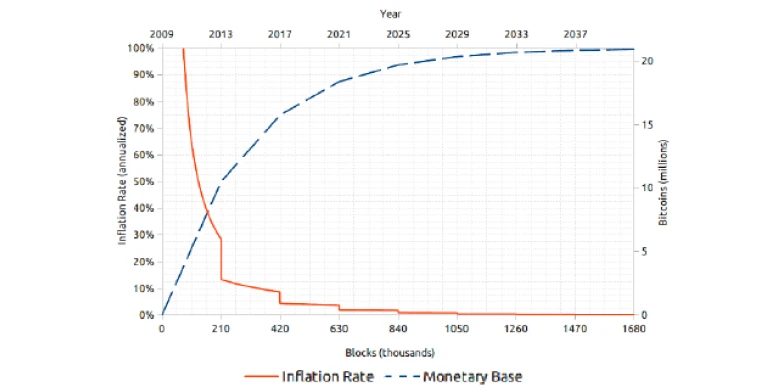
The chart below shows how BTC’s decline in inflation rate reached 50% at launch and will continue to drop to a projected 1% after 2032, thereby strengthening the 1% narrative.
With successive halvings, it currently sits close to 2% and is expected to drop to 1% and then to 0.5% after the 2032 halving. By then, more than 98.5% of BTC would have been mined, making it the most scarce monetary asset, ahead of gold, and strengthening the digital gold narrative.
Bitcoin as an Inflation Hedge — Myth, Reality, and Data
Historical Evidence
After 2020, when CPI inflation hit a peak high of 9.1% in the U.S following the COVID-19 pandemic, federal rate hikes suppressed Bitcoin as it plummeted to $17,000 from $69,000 in 2022. In 2023, it began to drop and was as low as 2.9% by December 2024. Bitcoin consequently rose to new all-time highs above $126,000 in 2025. In the last 5 years, the federal policies had a bigger impact on BTC than the actual CPI rates.
Though Bitcoin experienced more volatility in the last 5 years, its increase outperformed gold (~192%) and equities (~80-100%) during the same period, with growth exceeding 365% and an average of 80%, respectively. This makes Bitcoin more of a high-risk asset during short-term tightening cycles but acts as a reliable hedge during long-term debasement cycles.
Why Bitcoin Sometimes Fails as an Immediate Hedge
When institutions need urgent cash, selling Bitcoin is often the first option because it is a readily available market with high liquidity. When rates spike, speculative and risk-off markets take a dip as cash flows out of their markets into safe and stable markets.
During volatility spikes, institutional investors move to reduce portfolio risks by liquidating volatile assets, and Bitcoin is the most volatile asset. Hence, Bitcoin sometimes fails as an immediate hedge because it is not immune to crashing from short-term market volatility. But Bitcoin’s long-term trend has shown strong market valuation off a limited supply over prolonged market cycles.
Why Bitcoin Still Functions as a Long-Term Inflation Hedge
Bitcoin’s scarcity and 4-year halving cycles set it apart from fiat. Institutional giants are adopting it as a reserve asset, and its expanding ETF market makes it a long-term inflation hedge with scarcity-driven mechanisms like gold. Reliable Bitcoin prediction analyses have their value hitting as high as $250,000 by 2032.
Macro Trends Shaping Bitcoin’s Price Movements
Monetary Policy and Interest Rates
Federal, ECB, and global rate cuts and hikes influence BTC demand because investors have more cash to invest in Bitcoin, and massive rallies then follow the monetary expansion. This is why liquidity cycles (M2 expansion) have a strong say about Bitcoin rallies, as seen during the 2021 to 2022 rallies.
USD Strength and Inflation Hedging Behavior
When the dollar weakens, purchasing power weakens, making people move towards other reserve assets like Bitcoin and gold. This was evident during the 2020-2021 stimulus era when the dollar was debased to combat the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic: BTC surged in return.
ETF Demand and Institutional Allocation
Bitcoin ETFs function as a major vehicle for institutional investors to add Bitcoin to their portfolio and trade it in the financial markets. When investors expect inflation to rise, they accumulate BTC to hedge against USD debasement.
Geopolitical Tensions and Global Risk Cycles
With its lightning network layer-2 technology, Bitcoin powers fast and seamless cross-border payments across various countries. It thereby balances the geographical instability in countries with lagging transfer technologies.
Bitcoin vs Inflation Chart — What the Data Shows
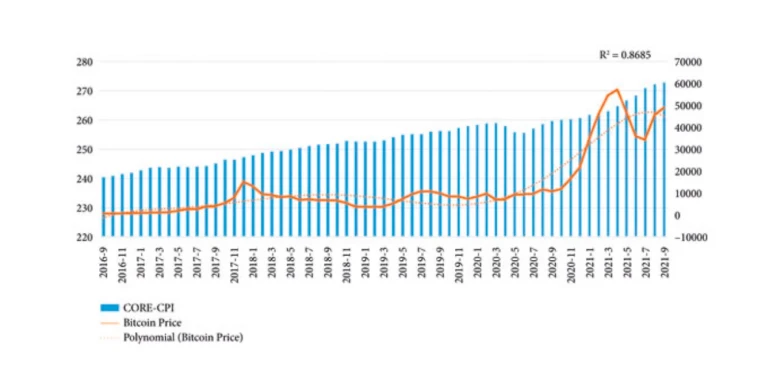
This chart shows that the CPI spikes do not directly drive BTC prices up. It is the federal rate cut that actually drives its price up from fiat debasement.
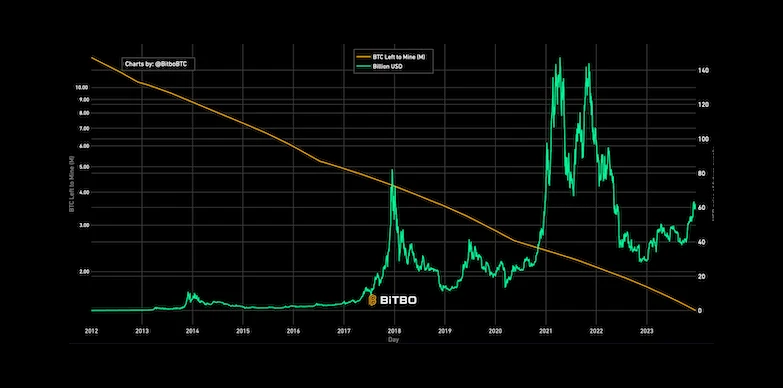
This chart shows the algorithmic halving system, which cuts the BTC inflation rate by 50% every 4 years, thereby creating unique supply shocks that drive the price up after every halving.
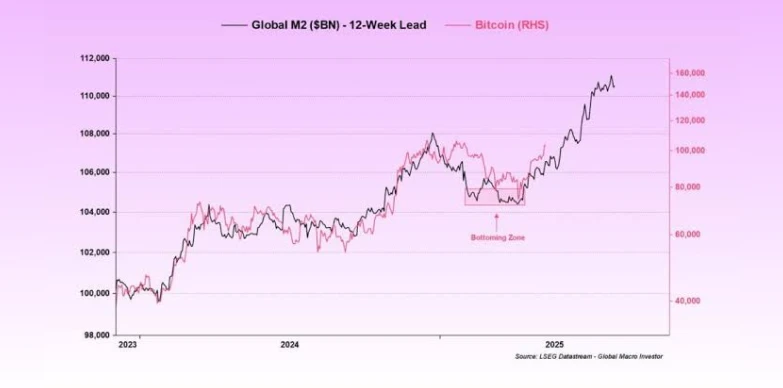
This chart shows the relationship between BTC price and M2 money supply. The production of more money to combat inflation causes the accumulation of scarce assets like Bitcoin, and their prices go up.
The Bitcoin vs inflation chart shows that CPI spikes connect to long-term Bitcoin rallies, but show the short-term price volatilities in the charts. Data-driven investors then make advanced Bitcoin predictions with a view to asymmetrical upside movements, not short-term price hikes.
How Inflation Shapes Bitcoin Price Predictions
Supply-Side Predictors
Every 4 years, the Bitcoin halving happens, reducing the inflation rate of Bitcoin and the supply rate, which is currently at 3.125 per block. This halving mechanism, in turn, shapes BTC price predictions in a particular cycle.
Demand-Side Predictors
Fiat currency debasement drives retail acquisition of Bitcoin; concurrently, institutional investors increase their holdings as a defensive measure against macroeconomic inflation. Nation-state interest is increasing, as shown by Argentina, El Salvador, and Turkey.
Macro Predictors
Federal interest rates, liquidity cycles, dollar strength, and crypto ETF adoptions driven by expected inflation are all macro factors that shape Bitcoin price predictions in the long run. Most analysts expect the price to respond strongly to long-term inflation cycles.
Is Bitcoin a Reliable Long-Term Hedge Against Inflation?
Bitcoin is highly volatile, and it works in the short term as a risk-on asset to control rate changes in the economy. In the long run, Bitcoin has proven to be a reliable hedge against inflation because of its limited supply, decentralized system, and immunity to government manipulation, just like gold. Hence, institutions now employ Bitcoin as a strategic “inflation insurance asset” by investing towards the 4-year cycle runs, which brings higher highs.
Risks and Limitations Investors Should Know
Investors should know that Bitcoin’s volatility is still high, and short-term money tightening cycles can temporarily dip BTC prices. Blockchain laws and regulations contain irregularities in some regions, affecting crypto trade freedom and adoption.
Investors should be aware that Bitcoin still depends on technological and network upgrades to reach its inflation and price target, and this can affect price behavior in some cycles.
Conclusion: Inflation Will Always Shape Bitcoin’s Future
Bitcoin is a long-term inflation hedge because of its algorithmic and predictable monetary policy through its 4-year halving system, which drives unique scarcity. Interest rates, liquidity, and fiscal policies will continue to swing Bitcoin’s price within market cycles. Price movements during short market cycles should be a signal to maximize Bitcoin’s asymmetric price highs in the long term.
References
- https://goldprice.org/gold-price-history.html
- https://www.nasdaq.com/articles/heres-average-stock-market-return-last-10-years-and-what-wall-street-expects-future
- https://forklog.com/en/in-argentina-turkey-and-beyond-crypto-doubles-as-an-inflation-hedge/amp/
- https://www.binance.com/en/events/bitcoin-halving